India is preparing to introduce a nationwide digital identity system for electric vehicle batteries, informally referred to as Battery Pack Aadhaar.
Under newly released draft guidelines, every eligible EV battery pack will be assigned a unique 21-character Battery Pack Aadhaar Number (BPAN) to enable end-to-end lifecycle tracking — from manufacturing to recycling.
This marks a major shift in how batteries are regulated, monitored, and valued in India’s rapidly expanding electric mobility ecosystem.


This article explains:
- What existed before BPAN
- What changes after BPAN
- What the system is for
- How it works technically
- Who it affects
- Why it matters for EV trucks, fleets, OEMs, recyclers, and policymakers
What Is Battery Pack Aadhaar (BPAN)?
Battery Pack Aadhaar is a proposed unique digital identity framework for EV and select industrial batteries introduced by the Government of India through draft technical guidelines.
Each battery pack will be issued:
- A 21-character alphanumeric Battery Pack Aadhaar Number (BPAN)
- A QR code physically affixed to the battery pack
- A digital record maintained on a centralized government-authorized platform
The goal is to treat batteries as traceable digital assets, not anonymous hardware components.
Before vs After: What Exactly Is Changing?
🔴 Before Battery Pack Aadhaar
| Area | Status Before |
|---|---|
| Battery identity | No unique ID per battery pack |
| Tracking | Limited to OEM internal records |
| Ownership history | Not traceable |
| Safety incidents | Fragmented reporting |
| Recycling | Informal, manual, hard to enforce |
| Counterfeit batteries | Difficult to detect |
| Second-life evaluation | Largely subjective |
🟢 After Battery Pack Aadhaar
| Area | Status After BPAN |
|---|---|
| Battery identity | Unique BPAN for every pack |
| Tracking | Manufacturing → usage → end-of-life |
| Ownership history | Digitally traceable |
| Safety incidents | Logged & auditable |
| Recycling | Enforceable & data-driven |
| Counterfeit control | Strong deterrence |
| Second-life use | Data-backed decisions |
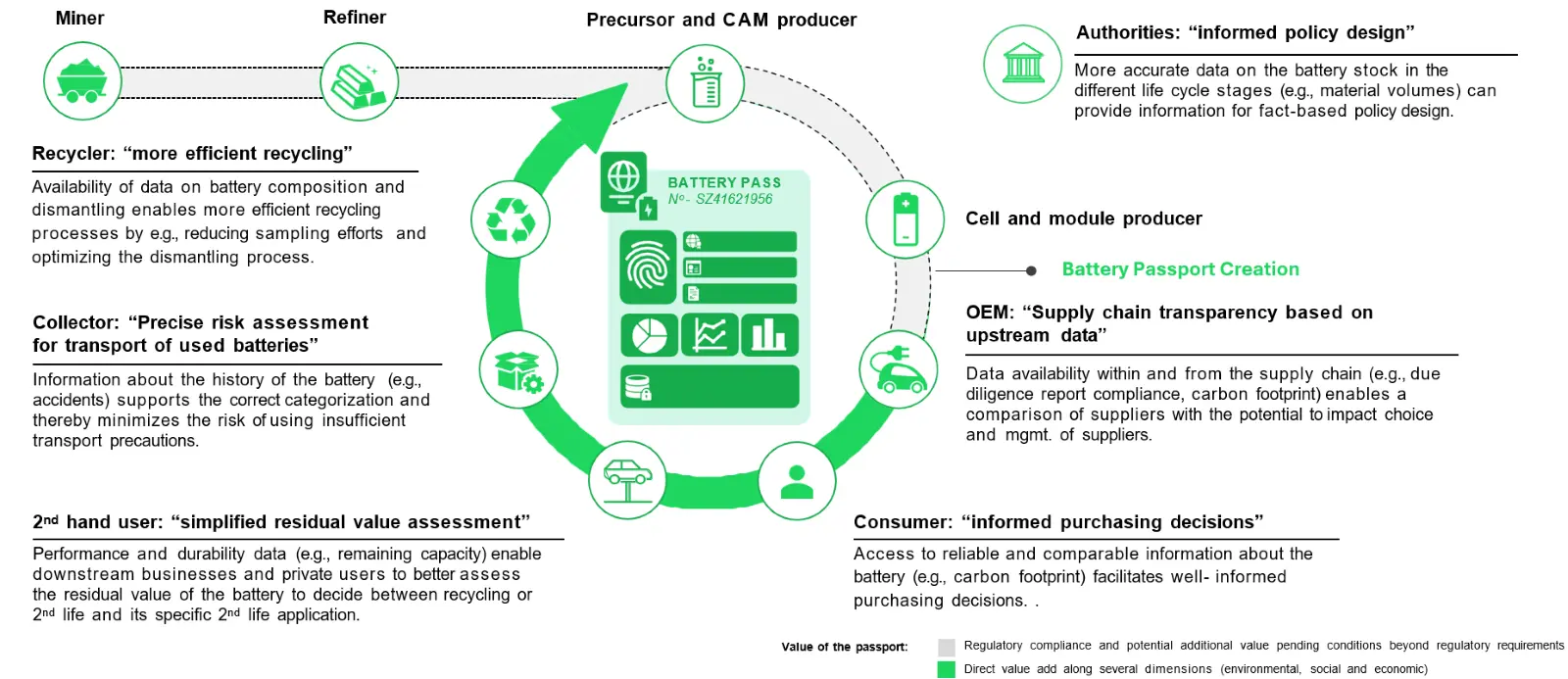
What Is Battery Pack Aadhaar Used For?
The BPAN framework serves five critical functions:
1️⃣ Lifecycle Traceability
Tracks a battery from:
- Manufacturer
- OEM integration
- Vehicle usage
- Second-life applications (if any)
- Recycling or disposal
This is essential for lithium-ion batteries, which are hazardous and resource-intensive.
2️⃣ Safety & Incident Monitoring
Dynamic data helps record:
- Thermal events
- Abnormal degradation
- Operating violations
- End-of-life status
This improves fire risk analysis, recalls, and preventive action.
3️⃣ Recycling & Circular Economy Enforcement
Recyclers can identify:
- Battery chemistry
- Material composition
- Remaining health
- Compliance history
This directly supports India’s battery waste management rules and circular-economy goals.
4️⃣ Counterfeit & Grey-Market Control
Each genuine battery pack becomes digitally verifiable, reducing:
- Fake battery circulation
- Unsafe replacements
- Warranty fraud
5️⃣ Policy & Manufacturing Oversight
BPAN strengthens:
- Domestic value-addition verification
- Enforcement under ACC PLI schemes
- National EV data intelligence
What Data Does BPAN Store?
The framework clearly separates data into static and dynamic categories.
🔹 Static Data (QR-Linked)
| Data Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Name, location |
| Battery specs | Capacity, voltage, chemistry |
| Material composition | Cell type, materials |
| Carbon footprint | Manufacturing emissions |
| Compliance | Standards followed |
🔹 Dynamic Data (Central Server – Restricted Access)
| Data Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| State of Health (SoH) | Battery ageing assessment |
| Charge-discharge cycles | Usage tracking |
| Thermal incidents | Safety analytics |
| End-of-life flag | Recycling trigger |
Dynamic data is not public and is accessible only to authorized stakeholders such as OEMs, service providers, and recyclers.
Who Must Issue and Use BPAN?
Covered Batteries
- EV traction batteries
- Select industrial batteries above defined capacity thresholds
Excluded
- Small portable batteries
- SLI (Starting, Lighting & Ignition) batteries
Responsibility
- Battery manufacturers and importers must generate BPAN
- BPAN must be permanently affixed to the battery pack
How the System Works (Simplified Flow)
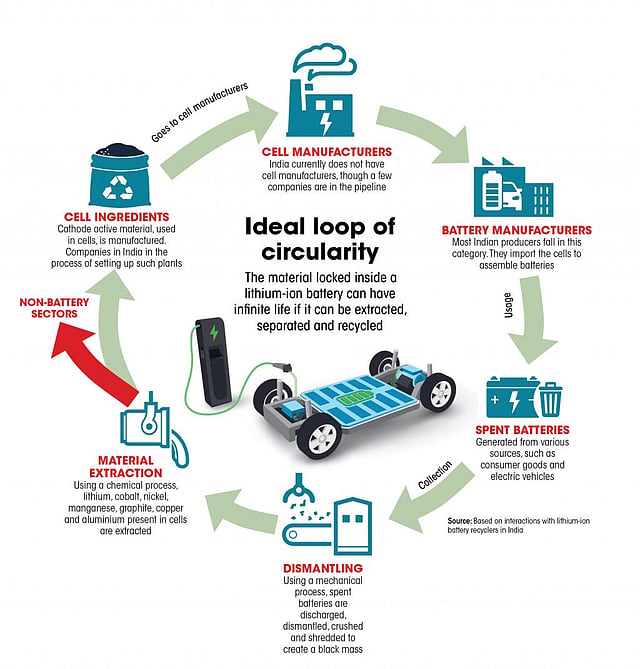
- Battery manufactured → BPAN assigned
- QR code fixed on battery pack
- Battery integrated into EV
- Usage data logged via BMS (where applicable)
- Ownership / service events recorded
- Battery flagged for second-life or recycling
- Recycler verifies BPAN before processing
How This Impacts EV Trucks & Commercial Fleets
For electric trucks, buses, and fleet vehicles, BPAN is especially significant:
- Better resale & residual value assessment
- Clear battery health transparency
- Reduced risk of unsafe replacements
- Easier compliance during audits
- More accurate total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis
Fleet operators will increasingly evaluate vehicles based on battery data integrity, not just upfront price.
Alignment with Global Standards
India’s Battery Pack Aadhaar mirrors concepts such as:
- EU Battery Passport
- Global battery traceability initiatives
But it is localized for Indian scale, cost sensitivity, and enforcement realities.
Official Reference Links (Government & Policy)
- Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH) – Draft guidelines
https://morth.nic.in - Automotive Industry Standards Committee (AISC)
https://aicte-india.org/aic - Battery Waste Management Rules (MoEFCC)
https://moef.gov.in
(Always refer to the latest official notifications for updates.)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is Battery Pack Aadhaar mandatory now?
No. The system is currently under draft guideline stage. Mandatory implementation will follow formal notification.
Will BPAN increase battery cost?
Direct cost impact is expected to be minimal, mainly related to compliance and data integration.
Is private user data shared publicly?
No. Only static battery identity data is visible via QR. Usage data remains restricted.
Does BPAN track vehicle location?
No. It tracks battery lifecycle data, not vehicle movement.
How does this help recycling?
Recyclers get verified data on chemistry, health, and origin, enabling safe and compliant processing.
Will this affect battery warranties?
Indirectly, yes. Accurate lifecycle data reduces disputes and misuse claims.
Final Takeaway
Battery Pack Aadhaar is a foundational regulatory shift.
It transforms EV batteries from:
Untraceable hardware → Verified digital assets
For India’s EV ecosystem — especially commercial EVs and electric trucks — BPAN lays the groundwork for:
- Safer operations
- Better policy enforcement
- Stronger recycling economics
- Data-driven battery valuation
This is not just regulation — it is infrastructure for battery intelligence.